Marking and Measuring Instruments
Rulers (stainless steel),15cm, Graduated in mm and inches..
$0.00
Rulers (stainless steel),20cm, Graduated in mm and inches..
$0.00
Rulers (stainless steel),30cm, Graduated in mm and inches..
$0.00
Rulers (stainless steel),50cm, Graduated in mm and inches..
$0.00
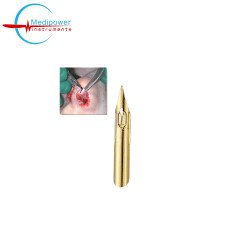
The Jameson Caliper is a compact and reliable measuring tool designed for precise internal, external, and depth measurements. With a measuring scale ranging from 0 to 80 mm..
$0.00
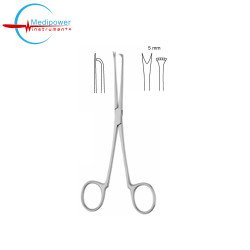
The Thorpe Caliper is a precision measuring instrument designed for accurate internal and external measurements. Featuring an angled jaw design, it allows easier access to recessed or hard-to-reach areas. With a total length of 11 cm, the caliper is compact yet practical for detailed measurement tas..
$0.00
The Pitanguy Facelift Marker is a specialized surgical marking instrument designed for precise preoperative planning in facelift and cosmetic procedures. With a length of 16 cm, it provides excellent control and reach during use...
$0.00
The Bone Bow Spacer is a surgical instrument designed to maintain controlled spacing and alignment during orthopedic or reconstructive procedures involving bone structures. With an overall length of 19.5 cm, it offers adequate reach and stability while allowing precise handling...
$0.00
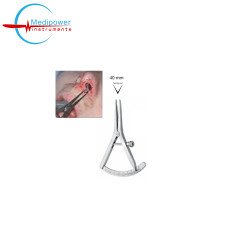
Castroviejo Calipers – 8 cm (20 mm)
The Castroviejo Calipers are precision measuring instruments commonly used in ophthalmic, microsurgical, and delicate surgical procedures. With an overall length of 8 cm and a measuring capacity of up to 20 mm, they are designed for highly accurate measurements i..
$0.00
The Castroviejo Calipers are precision measuring instruments commonly used in ophthalmic, microsurgical, and delicate surgical procedures...
$0.00